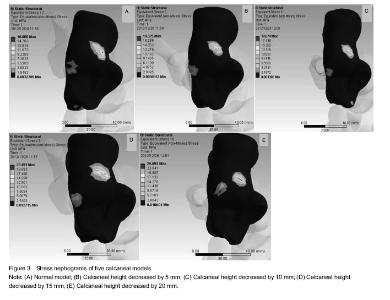
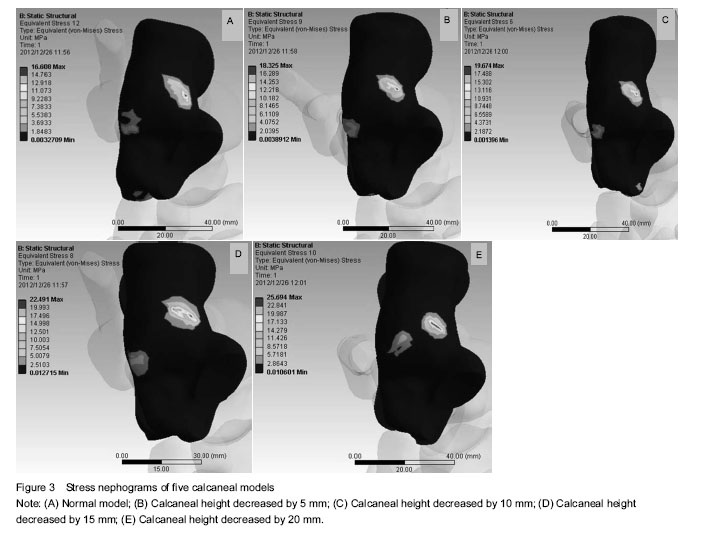
| [1] Yu GR, Yan XY. Selection of the calcaneal fractures treatment method. Zhonghua Guzhe Zazhi. 2006;26(2):134-141.
[2] Chen B, Liang RG, Wang G. Operative treatment of calcaneal fractures. Zhonghua Chuangshang Guzhe Zazhi. 2010;12(8):746-751.
[3] Yu GR. Treatment strategy of fracture for special heel topic. Shanghai Yixue. 2005;28(7):541-543.
[4] Wirtz DC, Pandorf T, Portheine F, et al. Concept and development of an orthotropic FE model of the proximal femur. J Biomech. 2003;36(2):289-293.
[5] Ulrich D, Hildebrand T, Van Rietbergen B, et al. The quality of trabecular bone evaluated with micro-computed tomography, FEA and mechanical testing. Stud Health Technol Inform. 1997;40:97-112.
[6] Lenaerts L, van Lenthe GH. Multi-level patient-specific modelling of the proximal femur. A promising tool to quantify the effect of osteoporosis treatment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2009;367(1895):2079-2093.
[7] Bessho M, Ohnishi I, Kaneko M, et al. Prediction of bone strength using a quantitative computed tomography based finite element method. Clin Calcium. 2011;21(7):1021-1027.
[8] San Vicente G, Buchart C, Borro D, et al. Maxillofacial surgery simulation using a mass-spring model derived from continuum and the scaled displacement method. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2009;4(1):89-98.
[9] Bandak FA, Vander Vorst MJ, Stuhmiller LM, et al. An imaging-based computational and experimental study of skull fracture: finite element model development. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(4):679-688.
[10] Harada A, Wakao N, Nemoto T. Bone structure and strength in the proximal femur - changes due to age and medical treatment. Clin Calcium. 2013;23(7):943-950.
[11] Mosekilde L. Normal age-related changes in bone mass, structure, and strength--consequences of the remodelling process. Dan Med Bull. 1993;40(1):65-83.
[12] Katsamanis F, Raftopoulos DD. Determination of mechanical properties of human femoral cortical bone by the Hopkinson bar stress technique. J Biomech. 1990; 23(11):1173-1184.
[13] Sowmianarayanan S, Chandrasekaran A, Kumar RK. Finite element analysis of a subtrochanteric fractured femur with dynamic hip screw, dynamic condylar screw, and proximal femur nail implants--a comparative study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(1):117-127.
[14] Li H, Zhang Y. Research advance of dynamic hip screw internal fixation in treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005;19(10): 839-842.
[15] Holstein JH, Garcia P, Histing T, et al. Advances in the establishment of defined mouse models for the study of fracture healing and bone regeneration. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(5 Suppl):S31-38.
[16] Kaplan K, Miyamoto R, Levine BR, et al. Surgical management of hip fractures: an evidence-based review of the literature. II: intertrochanteric fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(11):665-673.
[17] Zhang QH, Teo EC. Finite element application in implant research for treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease. Med Eng Phys. 2008;30(10):1246-1256.
[18] Kusz D, Okrajni J. Computer stimulation of stress distribution in finite element models of the normal femur and after Weller, Centrament, Parhofer-Mönch type prosthesis implantation. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2000;65(5):519-527.
[19] Taylor M, Bryan R, Galloway F. Accounting for patient variability in finite element analysis of the intact and implanted hip and knee: a review. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2013;29(2):273-292.
[20] Liu QH, Yu B, Jin D, et al. Construction and significance of finite element model of human ankle with complete anatomical structure. Shandong Yiyao. 2010;50(14):1-3.
[21] Wang YC. Bone and Joint Injuries. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. 2009.
[22] Ogut T, Ayhan E, Kantarci F, et al. Medial fracture line significance in calcaneus fracture. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011; 50(5):517-521.
[23] Goldzak M, Mittlmeier T, Simon P. Locked nailing for the treatment of displaced articular fractures of the calcaneus: description of a new procedure with calcanail(®). Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;22(4):345-349. |